Unit 1: F2F learning – Digital transformation and its effects

What does digital transformation bring?
Digital transformation is the process of integrating digital technologies into all aspects of an organization, from its operations and processes to its customer interactions and business models. However, with the increasing reliance on digital technology comes an increased risk of cyber threats. Cybersecurity is a critical component of any digital transformation strategy, as it ensures the protection of sensitive information and assets from malicious actors. It is essential for organizations to develop and implement robust cybersecurity protocols and best practices to mitigate the risk of cyber-attacks and protect their digital infrastructure. Failure to do so can result in significant financial, reputational, and legal consequences for organizations, highlighting the importance of cybersecurity in today’s digital age.
Increased need for digital transformation, global shift to distance work triggered by the pandemic and geopolitical situation have opened the hunting season for cybercriminals – targeted attacks on businesses, especially SMEs, are intensifying.
This unit will focus on the increased need for digital transformation and the consequences related to cybersecurity in the context of digital transformation and the introduction of new technologies. It will emphasise that introducing new technologies without addressing people and processes within a company or an organisation can open the door to cyber attackers.
Digital transformation is not just about technology. It is about people, optimisation, and the capability to rapidly adapt to current and future circumstances through different digital technologies in different environments and contexts (e.g. industry).
There are several different concepts of digital transformation, each with its own focus and approach. Here are a few examples:
- business process transformation – it involves using digital technology to streamline and automate business process, such as accounting, inventory management or customer service;
- customer experience transformation – it focuses on using digital technology to improve the customer experience, such as through the use of personalised marketing, digital self-service options, and real-time customer support (live-chat, messaging, phone);
- product and service innovation – it involves using digital technology to create new products and services that are innovative and better meet customer needs (such as smart homes, digital healthcare, online education, mobile banking etc.);
- data-driven decision making – it involves using data analytics and machine learning to make better business decisions, such as by predicting customer behaviour or optimising supply chain operations;
- organisational agility – it involves using digital technology to create a more agile and adaptable organisation, such as by implementing agile methodologies, digital collaboration tools and flexible work arrangements.
Overall, digital transformation involves using digital technology to transform organisations’ processes, operations and business models, with the goal of improving efficiency, innovation and customer satisfaction.

Different concepts of digital transformation
Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, refers to the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing and other industries. It builds on the previous three industrial revolutions that brought steam power, electricity, and computerization to the manufacturing sector.
Industry 4.0 is characterized by the integration of advanced technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics, to create “smart” factories and supply chains that are highly connected and automated. These technologies enable the collection and analysis of large amounts of data in real-time, enabling better decision-making, predictive maintenance, and personalized production.
Industry 4.0 is also characterized by the use of “cyber-physical systems,” which combine physical systems with digital technologies to create highly flexible and efficient production processes – “from a manufacturing industry perspective, a cyber-physical system is an internet-enabled physical entity, such as a pump or compressor, embedded with computers and control components consisting of sensors and actuators.” (Arcot, 2021)
According to Deloitte, “the term Industry 4.0 encompasses a promise of a new industrial revolution—one that marries advanced manufacturing techniques with the Internet of Things to create manufacturing systems that are not only interconnected, but communicate, analyze, and use information to drive further intelligent action back in the physical world.”
Overall, Industry 4.0 represents a major shift in the way that goods and services are produced and delivered, enabling greater efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness in the global marketplace. It has implications for various industries, such as automotive, healthcare, energy, and logistics, and is expected to have a significant impact on the global economy in the coming years.
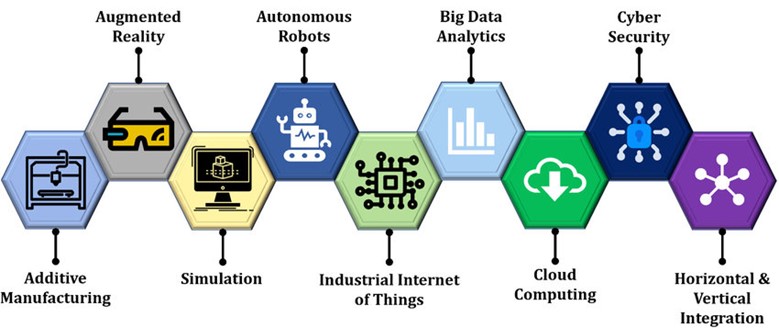
Figure 1. Enabling technologies of Industry 4.0. (available via license: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International)
The 9 key enabling technologies in Industry 4.0 are:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) – AI technologies such as machine learning and natural language processing are used to analyze and interpret data, make predictions, and automate decision-making.
- Big Data Analytics – the ability to collect and analyze vast amounts of data from sensors, machines, and other sources in real-time to gain insights and optimize processes.
- Cloud Computing – the use of shared computing resources and services over the internet to store, process, and manage data.
- Cybersecurity – protecting systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, theft, or damage.
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) – connecting machines, sensors, and devices in industrial settings to gather and share data, monitor performance, and automate processes.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) – using AR and VR technologies to enhance the visualization and understanding of complex data and processes, as well as to improve training and collaboration.
- Additive Manufacturing – also known as 3D printing, additive manufacturing allows for the creation of complex and customized parts and products on-demand, reducing the need for traditional manufacturing methods and supply chains.
- Autonomous Systems– robotics and other autonomous systems that can operate and make decisions without human intervention, increasing efficiency and reducing costs.
- Simulation – the use of virtual models and simulations to test and optimize processes, products, and systems before implementation in the real world.
Watch a short video about the future of IoT Security:
Industry 5.0
Industry 5.0 is a term that has been proposed as an extension of Industry 4.0, which is the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing and other industries. While Industry 4.0 focuses on the integration of advanced technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics, to create “smart” factories and supply chains, Industry 5.0 seeks to balance automation with human-centered design.
ndustry 5.0 aims to create a more collaborative and human-centered approach to manufacturing, where humans and machines work together to create products that are tailored to individual needs and preferences. This involves the use of advanced technologies, such as AI and robotics, to automate repetitive and dangerous tasks, while humans focus on tasks that require creativity, empathy, and problem-solving skills.
In manufacturing, robots have historically performed dangerous, monotonous, or physically demanding work, such as welding, painting in car factories and loading and unloading heavy materials in warehouses. However, as machines in the workplace become more intelligent and connected, Industry 5.0 aims to merge those cognitive computing capabilities with human intelligence and resourcefulness in joint operations.
Industry 5.0 also involves the integration of sustainable and ethical principles into the manufacturing process, such as reducing waste and emissions, ensuring fair working conditions, and respecting cultural diversity. This aligns with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals, which aim to promote economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental sustainability.
Overall, Industry 5.0 represents a new paradigm in manufacturing that seeks to balance automation with human-centered design and sustainability. While it is still a conceptual idea, it reflects a growing recognition of the importance of balancing technological progress with social and environmental responsibility.
Here we have an example:
Danish company Universal Robots staked its claim as the first industrial robot provider that works safely and effectively alongside humans. At the same time, industrial robots have traditionally operated separately from workers and behind safety cages. The company’s robots were first deployed alongside human workers in 2008 at Linatex, a technical plastics and rubber supplier for industrial applications.
The pairing of human and machine workers opens the door to countless opportunities in manufacturing. And since the use cases of Industry 5.0 are still in their relative infancy, manufacturers should be actively strategising ways to integrate human and machine workers to maximise the unique benefits.

Cybersecurity considerations: examples from the industry
In the context of cybersecurity, digital transformation refers to the process of integrating cybersecurity into all aspects of an organisation’s digital infrastructure and operations. This includes implementing robust cybersecurity protocols and best practices across all digital channels and technologies, such as cloud computing, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and mobile apps.
- Cloud computing – refers to the use of remote servers hosted on the internet to store, manage and process data, instead of relying on local servers and personal computers; it allows for greater scalability (the ability of a system, process or business to handle increased demand or growth without sacrificing performance or quality), flexibility and cost-efficiency in data management and computing.
- Internet of Things (IoT) – refers to a network of physical devices, vehicles, buildings and other objects embedded with sensors, software and connectivity that allows them to collect and exchange data; IoT enables the creation of smart systems and applications that can improve efficiency, productivity and convenience in various domains.
- Mobile apps – refers to software applications designed for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Mobile apps can provide a range of functionalities, such as communication, entertainment, productivity, and e-commerce, and can be downloaded and installed from app stores or websites.
Digital transformation also involves the use of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and big data analytics, to improve cybersecurity operations and reduce the risk of cyber-attacks. For example, AI and machine learning can be used to detect and respond to cyber threats in real-time, while big data analytics can be used to identify patterns and trends in cybersecurity incidents and vulnerabilities.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) – refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that can perform tasks that typically require human cognition, such as learning, reasoning, perception, and decision-making; AI can be applied in various domains, such as natural language processing, computer vision, robotics, and gaming.
- Machine learning – refers to a subset of AI that involves the use of algorithms and statistical models to enable machines to learn from data and improve performance on specific tasks without being explicitly programmed; machine learning is used in various applications, such as image recognition, speech recognition, fraud detection, and recommendation systems.
- Big data analytics – refers to the process of analysing and extracting insights from large and complex data sets, typically using advanced algorithms, machine learning techniques, and visualization tools; big data analytics can be used to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies in data, and to inform decision-making in various domains, such as marketing, healthcare, finance, and security.
Overall, digital transformation is essential for ensuring the security and protection of an organization’s digital assets, as cyber threats continue to evolve and become more sophisticated. By integrating cybersecurity into all aspects of digital transformation, organisations can create a more secure and resilient digital infrastructure, enabling them to better protect their sensitive information and assets from cyber threats.
Here we have few examples from the industry:
- Rise of Automotive Hacking
Modern vehicles nowadays come packed with automated software creating seamless connectivity for drivers in cruise control, engine timing, door lock, airbags and advanced systems for driver assistance. These vehicles use Bluetooth and WiFi technologies to communicate, which also opens them to several vulnerabilities or threats from hackers. Gaining control of the vehicle or using microphones for eavesdropping is expected to rise in 2022 with more automated vehicles. Self-driving or autonomous vehicles use a complex mechanism that requires strict cybersecurity measures.
- IoT with 5G Network: The New Era of Technology and Risks
With the advent and growth of 5G networks, a new era of interconnectivity will become a reality with the Internet of Things (IoT). According to Qualcomm, 5G is the 5th generation mobile network, a new global wireless standard after 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G networks, enabling a new kind of network that is designed to connect virtually everyone and everything together including machines, objects, and devices.
5G wireless technology is meant to deliver higher multi-Gbps peak data speeds, ultra-low latency, more reliability, massive network capacity, increased availability, and a more uniform user experience to more users. Higher performance and improved efficiency empower new user experiences and connects new industries.
This communication between multiple devices also opens them to vulnerabilities from outside influence, attacks or an unknown software bug. Even the world’s most used browser supported by Google, Chrome, was found to have serious bugs. 5G architecture is comparatively new in the industry and requires a lot of research to find loopholes to secure the system from external attacks. Every step of the 5G network might bring a plethora of network attacks that we might not be aware of. Here, manufacturers must be very strict in building sophisticated 5G hardware and software to control data breaches.
- Case Equifax
Examples from the industry show that cybersecurity breaches can be devastating for businesses. For instance, in 2017, Equifax, a credit reporting agency, suffered a data breach that exposed the personal information of 147 million customers. This breach resulted in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal penalties for the company.

Final thoughts
We must understand that the most significant factor when it comes to cyber attacks is and always will be the human factor – the impact of cyber attacks in this sense is not only financial and reputational but also social and psychological.
New technologies are being introduced into our environments (home, school, work) and are developing at a pace that is quite challenging to catch up with.
However, we want to emphasise that there is a solution:
“Employees are often considered the weakest link when organisations estimate their cybersecurity risk. However, shifting the focus to employees’ approaches that can be “part of the solution” rather than “the problem” affects organisations positively and builds resilience within them.” (Bada, 2022)
To protect your business/school/organization or yourself from cyber threats, it’s crucial to establish a comprehensive cybersecurity plan that includes risk assessment, employee training, network security, data protection, and incident response. Regular updates of software and hardware systems and creating a culture of security awareness can also help reduce the risk of cyber-attacks.